Introduction:
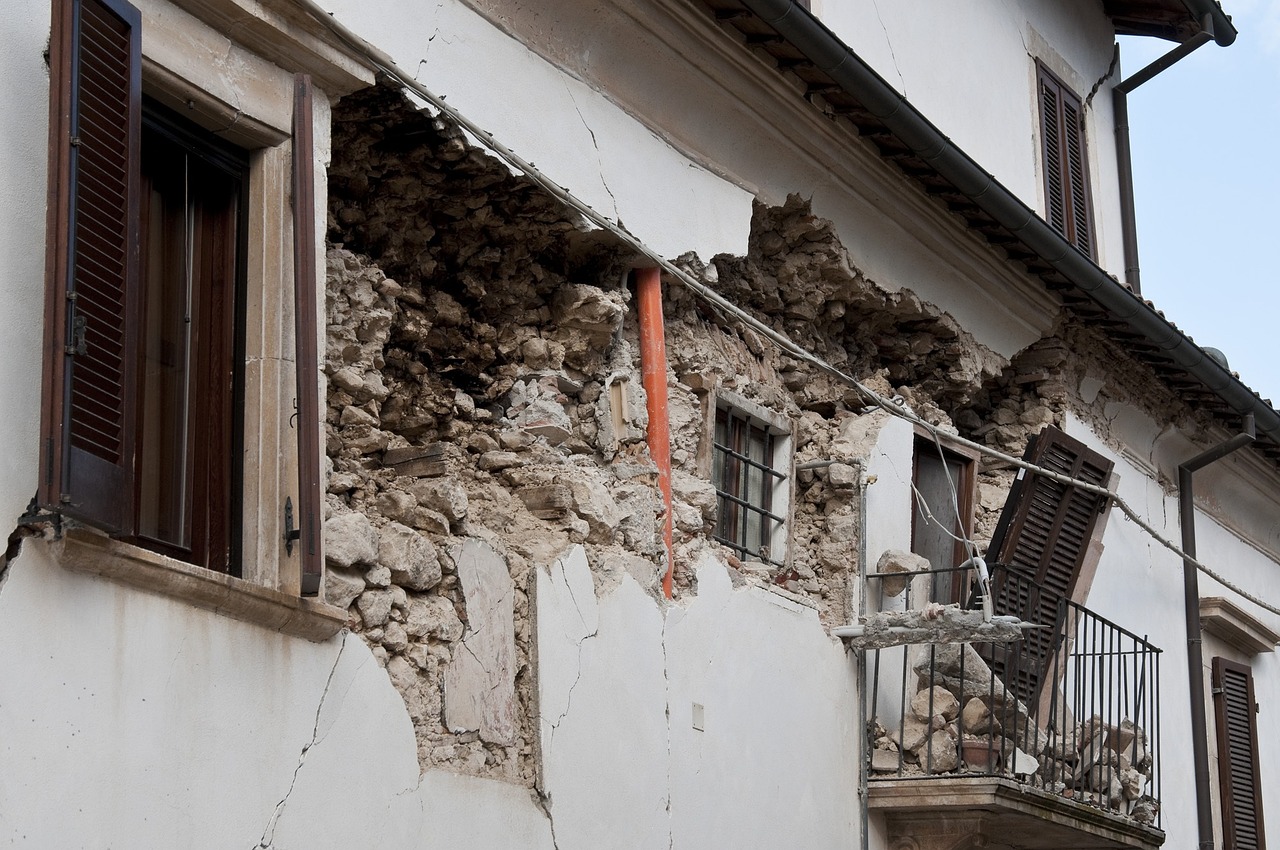
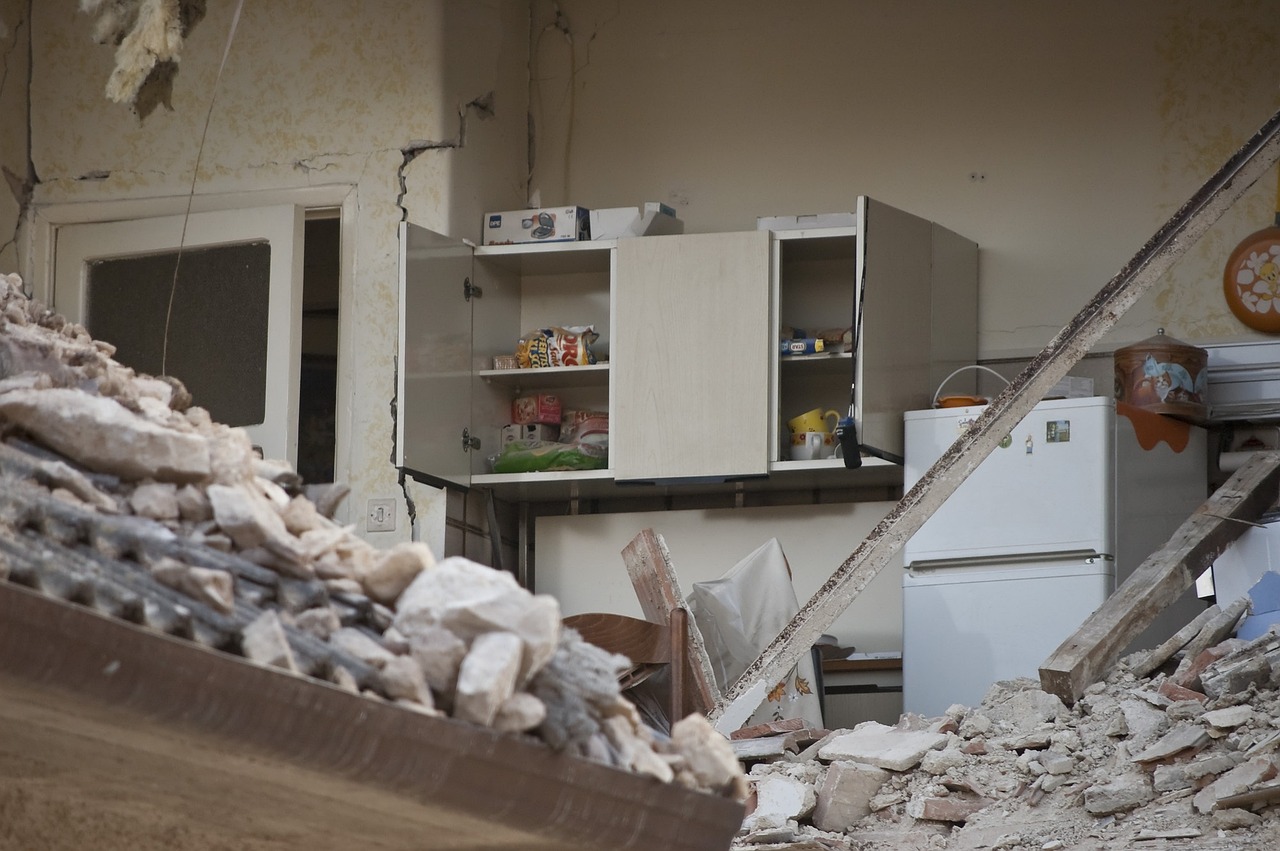
Building codes are critical tools for ensuring the structural integrity of buildings and protecting occupants from the devastating effects of earthquakes. In Oregon, a state situated in a seismically active region, evaluating and strengthening building codes for earthquake safety is paramount. In this blog, we will examine the importance of building codes in earthquake resilience and assess the efforts made in Oregon to enhance seismic preparedness through robust building regulations.
The Significance of Building Codes in Earthquake Safety:
Building codes establish minimum standards for the design, construction, and maintenance of structures to withstand various hazards, including earthquakes. Properly enforced building codes can significantly reduce the risk of structural failure and minimize casualties and property damage during seismic events. Key elements of earthquake-resistant building codes include requirements for reinforced foundations, structural framing, and seismic bracing.
Evaluating Building Codes in Oregon:
Oregon, situated in the seismically active Cascadia Subduction Zone, faces a heightened risk of earthquakes. Recognizing this threat, the state has implemented rigorous building codes aimed at enhancing earthquake resilience. The Oregon Structural Specialty Code (OSSC) incorporates seismic design provisions based on the latest scientific research and engineering practices. These provisions are continually updated to reflect advancements in seismic engineering and lessons learned from past earthquakes.
Strengthening Building Regulations:
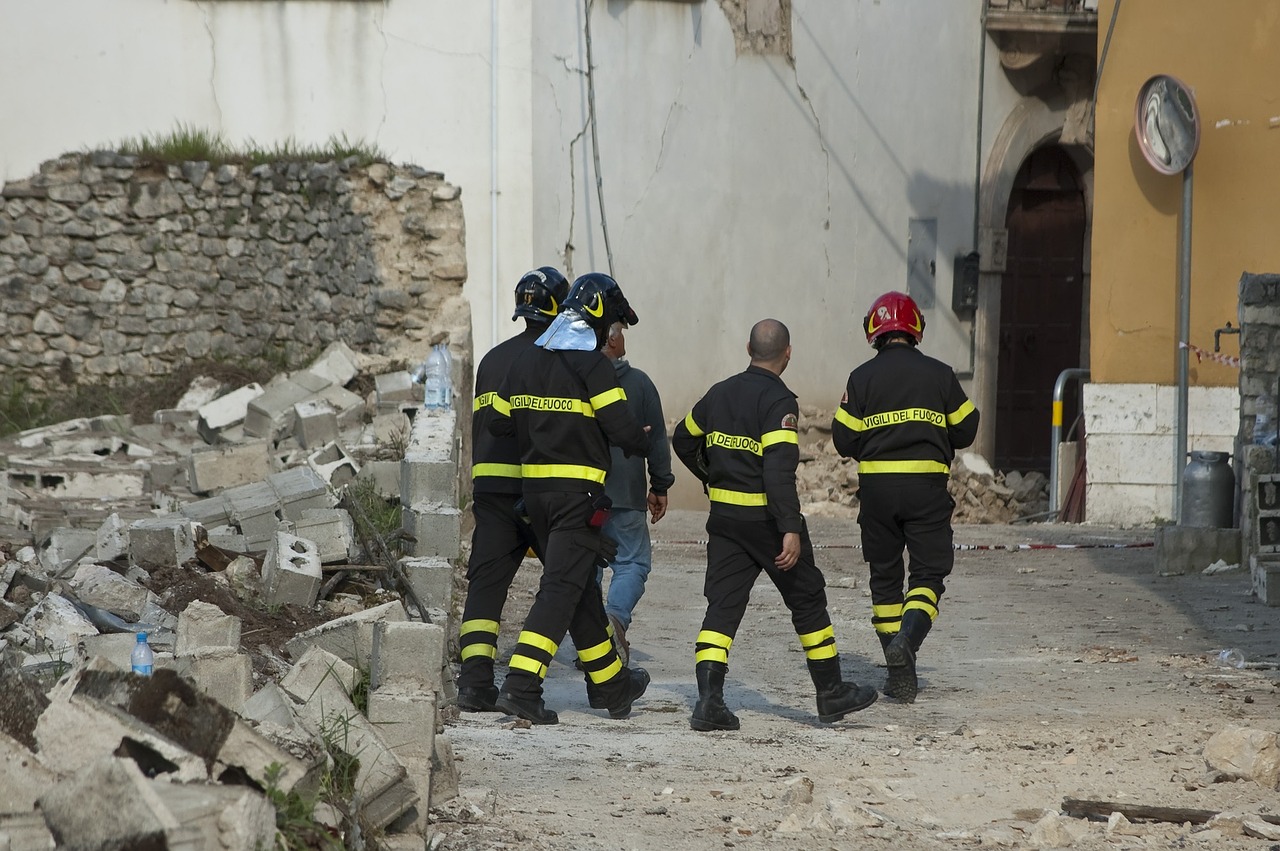
In recent years, Oregon has taken proactive measures to strengthen building regulations for earthquake safety. This includes adopting performance-based seismic design approaches that consider the specific characteristics of buildings and their expected performance during earthquakes. Additionally, the state has invested in seismic retrofitting programs to enhance the resilience of existing structures, particularly critical facilities such as schools, hospitals, and emergency response centres.
Challenges and Opportunities:
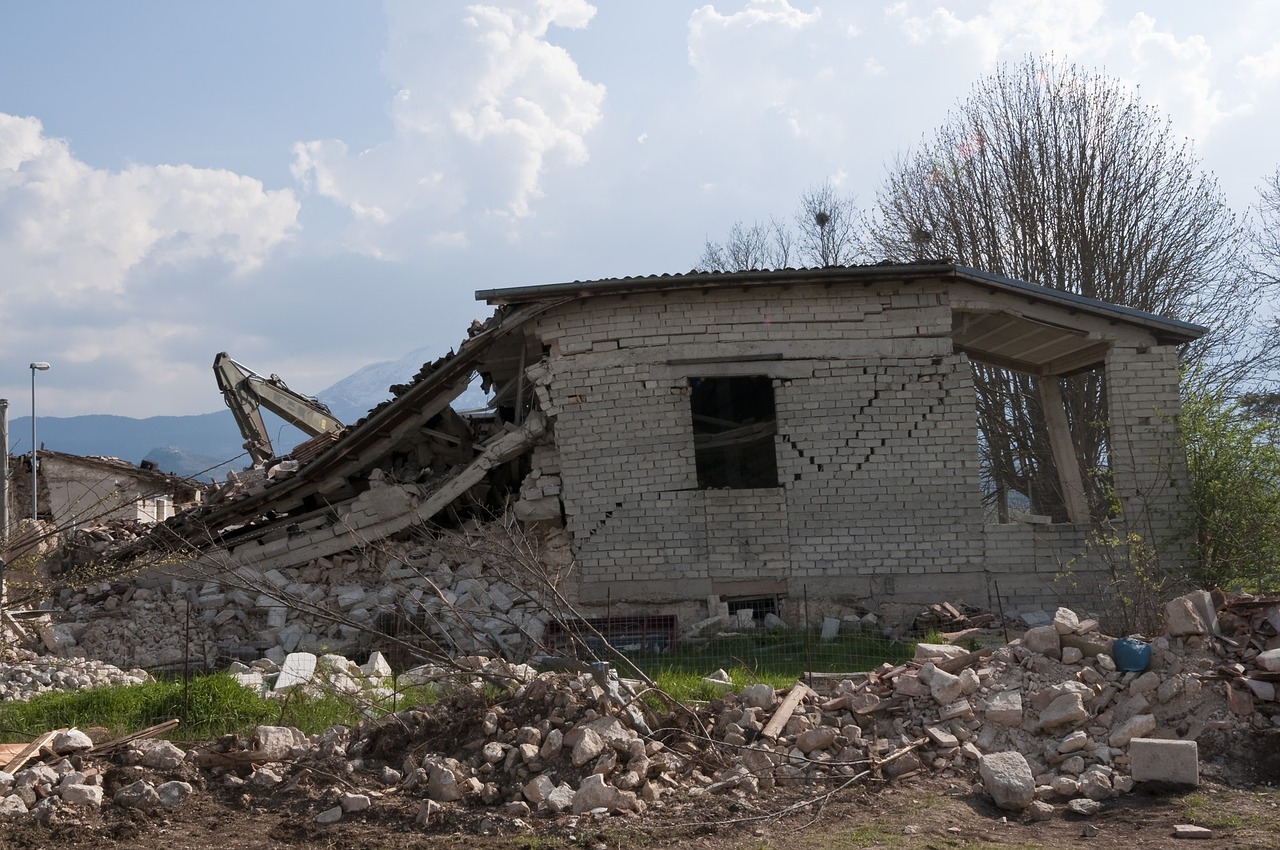
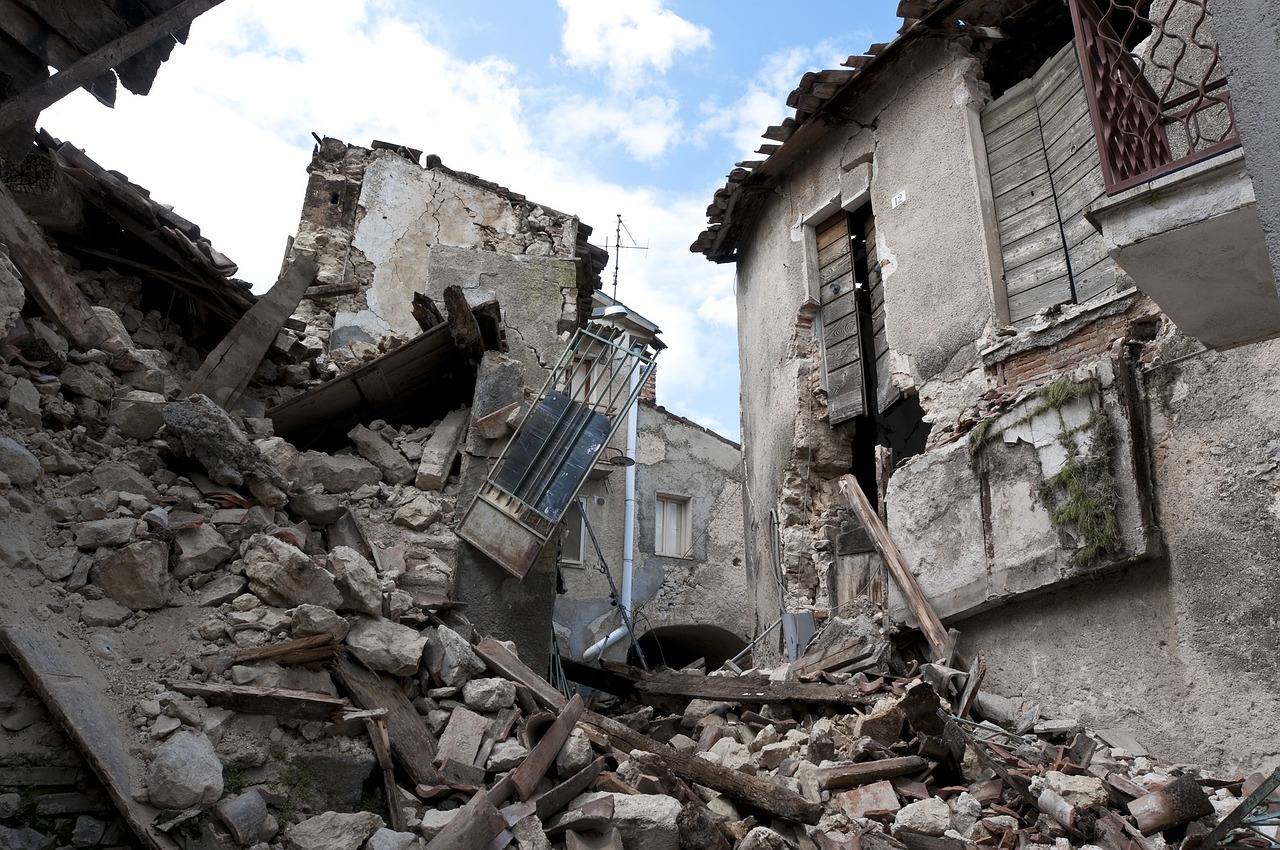
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in ensuring widespread compliance with earthquake-resistant building codes. Many older structures in Oregon may not meet current seismic standards, posing risks to occupants and communities. Addressing this issue requires a combination of regulatory enforcement, incentives for retrofitting, and public education campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of seismic resilience.
Conclusion:
Evaluating and strengthening building codes for earthquake safety is essential for mitigating the impacts of seismic events in Oregon and beyond. By adhering to robust seismic design standards, enforcing compliance with building codes, and investing in retrofitting efforts, Oregon can enhance the resilience of its built environment and protect the lives and livelihoods of its residents. Continued collaboration between policymakers, engineers, builders, and community stakeholders is crucial for advancing earthquake preparedness and ensuring the safety and resilience of Oregon’s built environment.